A pioneering camera and spectrometer for the James Webb Space Telescope - the gigantic successor to the Hubble Telescope - has just (18th August 2011) completed cryogenic testing at STFC's RAL Space in Oxfordshire. This testing subjected the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) to the harsh conditions it will experience when it is launched into space onboard the Webb Telescope.
The sophisticated instrument - designed to examine the first light in the Universe and the formation of planets around other stars - was put through its paces inside RAL Space's thermal space test chamber. MIRI contains a camera and a medium resolution integral field spectrograph and coronagraphs and it covers the wavelength range of 5 to 28 microns. This long wavelength range means that MIRI is unique among the Webb instruments because it has to be cooled to 7 Kelvin (minus 266 Celsius), which also brings tough challenges for testing the instrument.
Inside the RAL Space thermal space test chamber specially constructed shrouds cooled to 40K surround the instrument to represent properly the environment and background that the instrument will see in operation on Webb. Simulated stars are used to exercise thoroughly all the different ways in which scientists will use the instrument after launch. The tests were designed to ensure that MIRI can operate successfully in the cold vacuum of space and allow the MIRI scientists to gather vital calibration and baseline data. A team of more than 50 scientists from 11 countries have been working 24 hours a day 7 days a week for 3 months to complete the testing. The instrument has undergone the longest and most exhaustive testing at cryogenic temperatures prior to delivery of an astronomy instrument in Europe. With a total of 86 days at 7 Kelvin this is a significant achievement for the team operating the RAL Space test chamber.
"It is inspiring to see the MIRI working extremely well at its operating temperature after so many years in development. The test campaign has been a resounding success and the whole MIRI team can be very proud of this magnificent achievement" said Gillian Wright, the European Principal Investigator.
"The successful completion of this difficult test program - involving more than 2000 individual tests - marks a major milestone for the Webb telescope mission. The MIRI will now be delivered to NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center to join the integration and testing of the observatory's science instrument payload which began this year", said Matt Greenhouse, James Webb Space Telescope Project Scientist for the Science Instrument Payload, at NASA's Goddard, Greenbelt, Md.
The James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership between ESA, NASA and the Canadian Space Agency, is the next-generation premier space observatory, capable of exploring deep space phenomena from distant galaxies to nearby planets and stars. The Webb Telescope will enable scientists to "see the beginning" and study the formation of the Universe and the evolution of our own solar system, from the first light after the Big Bang to the formation of star systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth. The combination of Webb's unprecedented mirror size, cold temperature and location in space will make it the most powerful space observatory ever, which promises to revolutionise our view of the cosmos.
The Webb Telescope is central to the UK Space Agency's science programme which funds the UK's involvement in the project.
Dr David Parker, Director of Science, Technology and Exploration at the UK Space Agency, said, "MIRI will help unveil the early Universe with un-dreamed of detail; for astronomers, the Webb Telescope will be like a time machine allowing them to view the first stars and galaxies forming when the Universe was very young. It has taken a great deal of hard work and dedication from the European teams and JPL to get MIRI to this important milestone. With the UK playing a lead role in the instrument and the UK Astronomy Technology Centre being the overall European science lead for it, this project is a great example of how the specialist skills of our UK scientists and space companies are being utilised for the biggest and most ambitious international space projects."
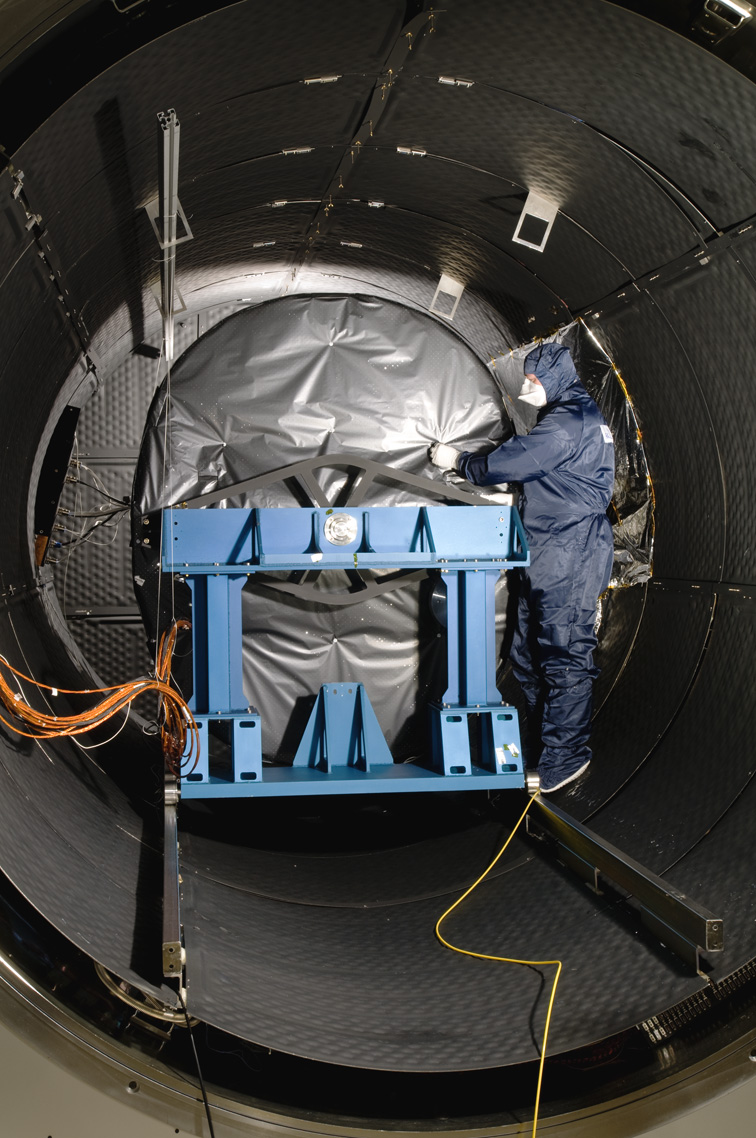

Image: MIRI in the thermal test chamber
(Credit: STFC RAL Space)
The STFC's UK Astronomy Technology Centre (UKATC) is leading the European team developing MIRI in a partnership with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Pasadena, Calif. A major part of the UK role is the Assembly Integration and Test (AIV) campaign at RAL Space. MIRI was integrated from key parts that have been developed at institutes across Europe and the USA. Each of these parts of MIRI have already, separately, undergone exhaustive testing to make sure they can survive the rigours of a journey into space and remain operational for the life of the mission. The test campaign at RAL is the only opportunity to ensure that all of the parts of the instrument function together properly and for scientists to obtain critical performance data before the launch. The extensive testing has generated simulated science data which will be used by astronomers in the coming years to develop the calibration software that will be needed when the instrument is in flight.
The MIRI team are now racing to analyse all the data from this huge cryogenic test campaign in parallel with completing the remaining warm testing and preparing the instrument for delivery to NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. There it will be integrated with the other instruments, the telescope and eventually the spacecraft.
MIRI's ultimate destination is L2 - a gravitational pivot point located four times further away from the Earth than the Moon, on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun. Here it is cool enough for MIRI's instruments to obtain the exquisite measurements that astronomers will use to help decipher the Universe.
Nobel Prize winner, Dr John Mather, Webb Senior Project Scientist at NASA Goddard said, "Thousands of astronomers will use the James Webb Space Telescope to extend the reach of human knowledge far beyond today's limits. Just as the Hubble Space Telescope rewrote textbooks everywhere, Webb will find new surprises and help to answer questions such as: How did a black hole get to the center of almost every galaxy, and how did it grow? What were the first objects to light up after the Big Bang? How did galaxies like the Milky Way come to their present shapes? When and where were the chemical elements of life synthesized, and how soon could planets and life appear after the Big Bang? How are stars like the Sun and planets like the Earth formed, and how unique is the Earth? Webb is about beginnings, the beginnings of everything."
MIRI will provide enormous increases in sensitivity, spatial and spectral resolution, enabling astronomers to identify the very earliest galaxies. The astronomers who will use MIRI and the Webb telescope are also particularly keen to explore the formation of planets around distant stars. The emission from such events is shrouded by gas and dust in interstellar space. This is not a problem for MIRI, as the infrared light from these objects will penetrate these obstructions and allow MIRI to build up highly resolved images of planetary nurseries in unprecedented detail. With its spectrometer, MIRI could even reveal the existence of water and/or hydrocarbons on these planets or within the planetary debris, paving the way for investigations into the habitability of other planetary systems.
Notes for editors
Contacts
-
Gillian Wright
European Principal Investigator for MIRI
STFC UK Astronomy Technology Centre
Tel: +44 (0)131 668 8248
-
Julia Short
Press Officer
UK Space Agency
Tel: +44 (0)1793 418 069
The UK and MIRI
The UK's lead role for Europe in the instrument involves taking responsibility for the overall science performance, the mechanical, thermal and optical design, along with the assembly, integration, testing and calibration. These roles are shared between the UK institutions in the partnership as follows:
- UK Astronomy Technology Centre (UKATC), Edinburgh is the European science lead for the instrument; responsible for the overall instrument design, optical design and analyses, developing the overall calibration, and providing the spectrometer pre-optic subsystem.
- Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL), Oxfordshire is responsible for overall Optical System thermal design and analysis, and production of all thermal hardware; assembly, integration, testing & verification of instrument including provision of bespoke test facilities.
- University of Leicester is responsible for overall mechanical design and analysis; provision of instrument primary structure (in partnership with Danish National Space Centre); provision of mechanical ground support equipment.
- EADS Astrium provide the overall project management and engineering leadership role; systems engineering; overall instrument product assurance leadership.
The James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope is a joint project of NASA, ESA and the Canadian Space Agency. It will carry four scientific instruments: MIRI (mid-infrared camera and spectrograph), NIRSpec (near-infrared spectrograph), NIRCam (near-infrared camera), and TFI (tunable filter imager).
MIRI
MIRI, the mid-infrared instrument, provides imaging, coronagraphy and integral field spectroscopy over the 5-28 micron wavelength range. It is being developed as a partnership between Europe and the USA - the partners being a consortium of nationally funded European institutes, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), ESA and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC).
MIRI development draws on the expertise of the following organisations:
- Ames Research Center, USA;
- Astrium, Ltd, UK;
- ASTRON, Netherlands Foundation for Research in Astronomy;
- CEA Service d’Astrophysique, Saclay, France;
- Centre Spatial de Liége, Belgium;
- Consejo Superior de Investigacones Científicas, Spain;
- Cranfield University, UK;
- Danish Space Research Institute;
- Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Ireland;
- ETKA, Belgium;
- ESTEC, Netherlands;
- Institute d’Astrophysique Spatiale, France;
- Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aerospacial, Spain;
- ETH, Zurich, Switzerland;
- Jet Propulsion Laboratory, USA;
- Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille (LAM), France;
- Lockheed Advanced Technology Center, USA;
- Max-Planck-Insitut für Astronomie (MPIA), Heidelberg, Germany;
- Observatoire de Paris, France;
- Observatory of Geneva, Switzerland;
- Paul Scherrer Institut, Switzerland;
- Onsala Space Observatory, Sweden;
- Physikalishes Institut, Bern, Switzerland;
- Raytheon Vision Systems, USA;
- Space Telescope Science Institute, USA;
- STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL), UK;
- STFC UK Astronomy Technology Centre (UK ATC), UK;
- Toegepast-Natuurwetenschappelijk Ondeszoek (TNO-TPD), Netherlands;
- University of Amsterdam, Netherlands;
- University of Arizona, USA;
- University of Cardiff, UK;
- University of Cologne, Germany;
- University of Groningen, Netherlands;
- University of Leicester, UK;
- University of Leiden, Netherlands;
- University of Leuven, Belgium;
- University of Stockholm, Sweden;
- University of Reading, UK;
- Utah State University USA;
- Zeiss, Germany
The MIRI development is supported by the following national agencies:
- Belgian Science Policy Office (BELSPO)
- Centre Nationale D’Etudes Spatiales (CNES)
- Danish National Space Centre
- Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft-und Raumfahrt (DLR)
- Enterprise Ireland
- ESA
- Ministerio De Education y Ciencia
- NASA
- Nova
- STFC
- Swiss Space Office
- Swedish National Space Board
- UK Space Agency
UK Space Agency
The
UK Space Agency (link opens in a new window) is at the heart of UK efforts to explore and benefit from space. It is responsible for all strategic decisions on the UK civil space programme and provides a clear, single voice for UK space ambitions.
The UK's thriving space sector contributes £7.5bn a year to the UK economy, directly employs 24,900 and supports a further 60,000 jobs across a variety of industries.
The UK Space Agency:
- Co-ordinates UK civil space activity
- Encourages academic research
- Supports the UK space industry
- Raises the profile of UK space activities at home and abroad
- Increases understanding of space science and its practical benefits
- Inspires our next generation of UK scientists and engineers
- Licences the launch and operation of UK spacecraft
- Promotes co-operation and participation in the European Space programme
Learn more about STFC, visit STFC website.
For more information please contact:
RAL Space Enquiries